Spark Streaming RDD: Discretized Streams (DStream)
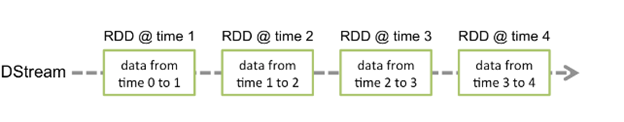
Discretized Stream or DStream is the basic abstraction provided by Spark Streaming. It represents a continuous stream of data, either the input data stream received from source, or the processed data stream generated by transforming the input stream. Internally, a DStream is represented by a continuous series of RDDs, which is Spark’s abstraction of an immutable, distributed dataset . Each RDD in a DStream contains data from a certain interval, as shown in the following figure:
Any operation applied on a DStream translates to operations on the underlying RDDs. For example, in the earlier example of converting a stream of lines to words, the flatMap operation is applied on each RDD in the lines DStream to generate the RDDs of the words DStream. This is shown in the following figure.
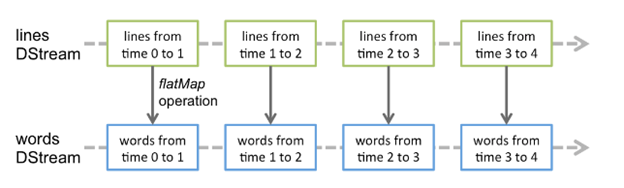
Transformations on DStreams
DStream operations are detaily described in the original documentation.
Similar to that of RDDs, transformations allow the data from the input DStream to be modified. DStreams support many of the transformations available on normal Spark RDD’s. Some of the common ones are as follows.
| Transformation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| map(func) | Return a new DStream by passing each element of the source DStream through a functionfunc. |
| flatMap(func) | Similar to map, but each input item can be mapped to 0 or more output items. |
| filter(func) | Return a new DStream by selecting only the records of the source DStream on whichfuncreturns true. |
| repartition(numPartitions) | Changes the level of parallelism in this DStream by creating more or fewer partitions. |
| union(otherStream) | Return a new DStream that contains the union of the elements in the source DStream andotherDStream. |
| count() | Return a new DStream of single-element RDDs by counting the number of elements in each RDD of the source DStream. |
| reduce(func) | Return a new DStream of single-element RDDs by aggregating the elements in each RDD of the source DStream using a functionfunc(which takes two arguments and returns one) The function should be associative and commutative so that it can be computed in parallel. |
| reduceByKey(func, [numTasks]) | When called on a DStream of (K, V) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, V) pairs where the values for each key are aggregated using the given reduce function. |
| join(otherStream, [numTasks]) | When called on two DStreams of (K, V) and (K, W) pairs, return a new DStream of (K, (V, W)) pairs with all pairs of elements for each key. |
Output Operations on DStreams
Output operations allow DStream’s data to be pushed out to external systems like a database or a file systems. Since the output operations actually allow the transformed data to be consumed by external systems, they trigger the actual execution of all the DStream transformations (similar to actions for RDDs). Currently, the following output operations are defined:
| Output Operation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| print() | Prints the first ten elements of every batch of data in a DStream on the driver node running the streaming application |
| saveAsTextFiles(prefix, [suffix]) | Save this DStream's contents as text files. The file name at each batch interval is generated based on prefix and suffix: "prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]". |
| saveAsObjectFiles(prefix, [suffix]) | Save this DStream's contents asSequenceFilesof serialized Java objects. The file name at each batch interval is generated based on prefix and suffix:"prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]". |
| saveAsHadoopFiles(prefix, [suffix]) | Save this DStream's contents as Hadoop files. The file name at each batch interval is generated based onprefixandsuffix:"prefix-TIME_IN_MS[.suffix]". Python APIThis is not available in the Python API. |
| foreachRDD(func) | The most generic output operator that applies a function, func, to each RDD generated from the stream. This functio should push the data in each RDD to an external system, suchas saving the RDD to files, or writing it over the network t a database. Note that the functionfuncis execute in the driver process running the streaming application, and will usually have RDD actions in it that will force the computation of the streaming RDDs. |